Landfill gas is an inevitable byproduct of waste decomposition. As waste breaks down, it releases gases under pressure, seeking an escape. Without proper systems, these gases can travel in unpredictable ways.
Let’s consider what landfill gas is, the potential risks it poses, and how we can effectively manage it.
What is Landfill Gas?
Landfill gas is primarily composed of methane and carbon dioxide, with trace amounts of other gases. These gases are constantly produced as organic waste decomposes. It’s crucial to direct these emissions into a landfill gas collection system, but gases can still find other escape routes.
Imagine a green haze spreading out from the landfill’s base, sides, and surface, representing how gases will migrate outward from the landfilled waste unless restrained by a containment membrane to prevent it from spreading.
Ontario regulations require that the methane soil vapour concentration be less than 2.5% by volume at the landfill’s property line. Monitoring soil gas probes around the landfill perimeter is standard practice to ensure these levels are maintained.

Pathways of Landfill Gas Migration
Landfill gas can move through porous soils and exploit continuous pathways like utility tunnels, acting as highways for gas. It’s vital to be aware of these pathways during site planning to prevent unintended gas movement. Landfill covers also play a role. Passive venting may encourage gas release from the top, whereas active collection systems should limit gas escape.
Paved surfaces can impede gas penetration, causing it to spread sideways until it dissipates. However, cracks in foundations or surfaces can act as entry points for gas into structures, posing risks to human health.
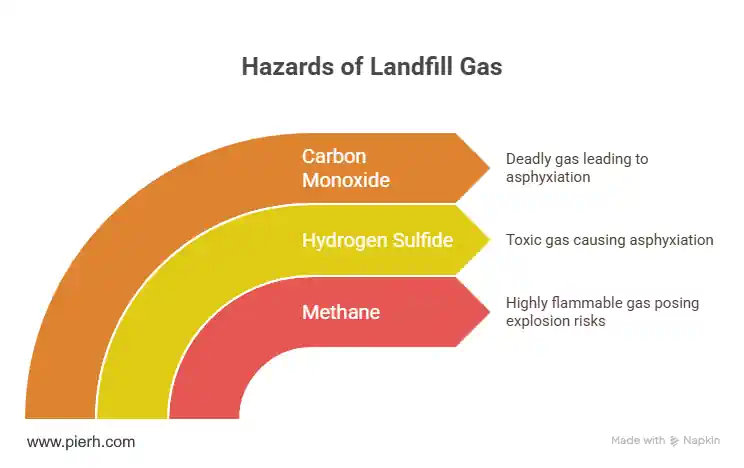
Risks of Landfill Gas
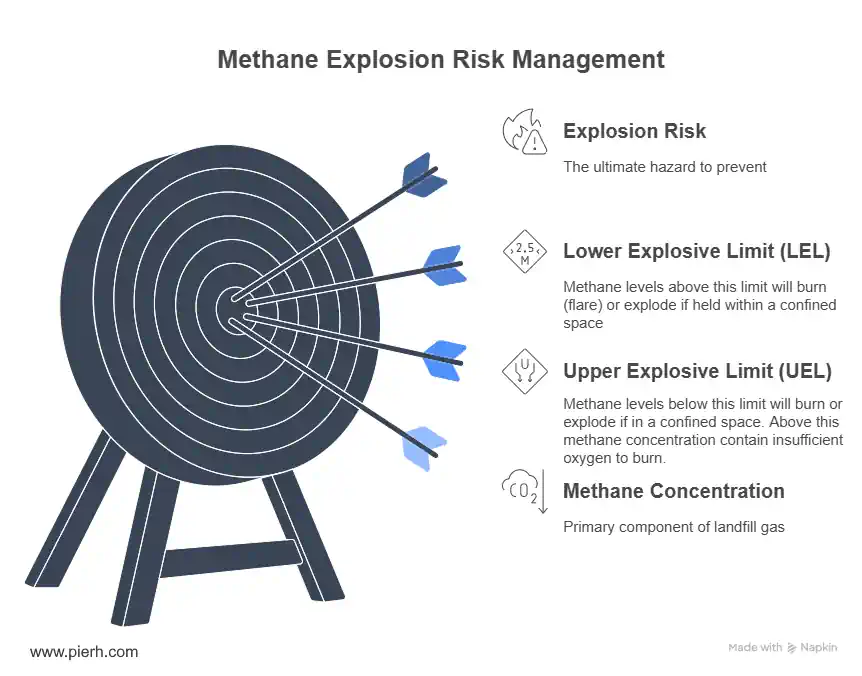
Explosion and Flammability: Methane is flammable between 5% and 17% by volume. Within landfills, concentrations should remain above the upper explosive limit to prevent ignition. Outside, they should stay below the lower limit to avoid explosions.
Toxicity and Asphyxiation: Landfill gas isn’t just a flammability concern; it’s also toxic. Hydrogen sulfide and carbon monoxide in landfill gas can be lethal at low concentrations. Even without acute symptoms, long-term exposure to trace chemicals can have health implications.
Managing Landfill Gas
Effective management involves maintaining landfill covers to prevent gas escape. A well-maintained cover with healthy vegetation can oxidize methane, reducing emissions. However, gas can dry out covers and create cracks, leading to further gas release. It’s a delicate balance of maintaining integrity and allowing controlled venting.
Advanced landfill gas management systems often employ both passive and active control measures. Passive systems rely on natural processes, such as diffusion and convection, to direct gas emissions to the atmosphere safely.
These systems are typically easier to maintain and cost-effective, but do not capture most of the greenhouse gas emiitted. Active systems, on the other hand, utilise mechanical means, such as extraction wells and collection pipes, to capture and transport landfill gas to treatment facilities. These systems are more efficient in gas capture but require regular maintenance and operational oversight to ensure their effectiveness.
Beyond the immediate health and safety concerns, landfill gas poses significant environmental challenges, particularly concerning climate change. Methane, the primary component of landfill gas, is a potent greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential significantly higher than carbon dioxide over a short-term period.
By effectively managing landfill gas emissions, we not only protect public health but also contribute to global efforts to mitigate climate change.
Technological advancements have facilitated the conversion of landfill gas into energy, providing a dual benefit of reducing emissions and generating renewable energy. This process involves collecting landfill gas and treating it to remove impurities, allowing it to be used as a fuel source for generating electricity or heat.
Landfill gas-to-energy projects have gained traction globally as they offer an economically viable and environmentally friendly solution to landfill gas management.
Community engagement and public awareness are also vital components of successful landfill gas management strategies. Educating local communities about the potential hazards of landfill gas and the measures taken to mitigate these risks can foster public support for landfill gas management initiatives.
Moreover, involving the community in monitoring efforts can enhance transparency and build trust between landfill operators and the public.
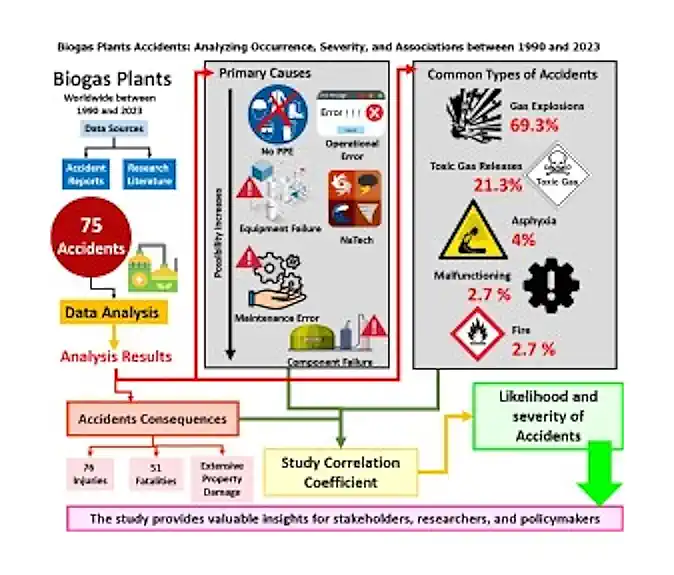
“Biogas plants accidents: Analyzing …” from www.sciencedirect.com and used with no modifications.
Landfill Gas Hazards Conclusion
In summary, responsible landfill gas management is crucial for safety and environmental health. By understanding the pathways and risks and implementing effective collection and monitoring systems, we can mitigate the dangers of landfill gas.
It requires a comprehensive approach that combines technological solutions, regulatory compliance, community engagement, and ongoing monitoring to ensure that landfill gas emissions are effectively managed and minimised.
Landfill Gas Hazards FAQs
What is landfill gas composed of? Landfill gas mainly consists of methane and carbon dioxide, with small amounts of other gases.
Why is methane dangerous? Methane is flammable between 5% and 17% concentrations, posing explosion risks. It’s also an asphyxiant, displacing oxygen.
How can landfill gas affect human health? Beyond explosion risks, gases like hydrogen sulfide and carbon monoxide can be toxic and lethal, even at low concentrations.
How do landfill gas collection systems work? These systems capture gas emissions, directing them away from the landfill to prevent uncontrolled release and reduce environmental impact. They can convert landfill gas into renewable energy, helping to mitigate climate change.
What are the regulations for landfill gas in Ontario? Methane concentrations must be below 2.5% at the landfill’s edge and less than 0.05% in buildings off-site, as per Ontario regulations.
How can communities contribute to landfill gas management? Communities can play a role by staying informed about landfill operations, participating in public consultations, and supporting efforts to reduce waste and enhance landfill gas capture and utilization.
What are some innovations in landfill gas management? Recent innovations include improved gas collection systems, advanced monitoring technologies, and enhanced gas-to-energy conversion processes, all aimed at maximising gas capture and minimising environmental impact.
The challenge of managing landfill gas effectively is ongoing, requiring vigilance, innovation, and collaboration between various stakeholders. By remaining committed to best practices and continuously exploring new solutions, we can address the hazards of landfill gas while harnessing its potential as a resource.
What is the Best Clean Energy Source for the Environment?
Explore the best clean energy alternatives that are good for the environment. Learn about the latest developments in renewable power technology.
Digester Mixing Theory And Landia GasMix Review
An Evaluation of the Landia GasMix and Principles of Digester Mixing Are you facing issues with your anaerobic digestion plant? Maybe it’s not producing as much biogas as you expected. One key factor could be the mixing system. Mixing is crucial for breaking down waste to produce biogas efficiently. A fact worth noting – effective […]
Exploring Biogas Examples: Learn How Organic Waste Can Fuel Energy Production
In this article we are exploring biogas examples read on and learn how organic waste can fuel energy. Production Biogas is a type of gas that comes from rotting stuff like leftover food and animal poo. People make it by letting these things break down without any air around. It’s mostly made of two gases […]
Green Energy from Brownfield Developments and Food Waste: A Sustainable Solution
Green energy from brownfield developments and food waste is a novel idea for an innovative and extremely sustainable alternative. Read on, and we will explain why. Climate change is an undeniable reality, with severe impacts on ecosystems and weather patterns, affecting coral reefs and bee populations, to name just two of the innumerable negative impacts, […]






